LISP and VXLAN
SD-Access Operational Plane
Control Plane - Lisp
Messaging and communication protocol between infrastructure devices in the fabric.
In these networks, the IP address is used for both network layer identification (who the device is on the network) and as a network layer locator (where the device is at in the network or to which device it is connected). This is commonly referred to as addressing following topology.
While an endpoint’s location in the network will change, who this device is and what it can access should not have to change. The Locator/ID Separation Protocol (LISP) allows the separation of identity and location though a mapping relationship of these two namespaces: an endpoint’s identity (EID) in relationship to its routing locator (RLOC).
Data Plane - VXLAN
Encapsulation method used for the data packets.
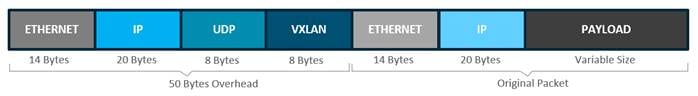
VXLAN is an encapsulation technique for data packets. When encapsulation is added to these data packets, a tunnel network is created.
Tunneling encapsulates data packets from one protocol inside a different protocol and transports the original data packets, unchanged, across the network.
A lower-layer or same-layer protocol (from the OSI model) can be carried through this tunnel creating an overlay. In SD-Access, this overlay network is referred to as the fabric.
VXLAN is a MAC-in-IP encapsulation method. It provides a way to carry lower-layer data across the higher Layer 3 infrastructure. Unlike routing protocol tunneling methods, VXLAN preserves the original Ethernet header from the original frame sent from the endpoint.
This allows for the creation of an overlay at Layer 2 and at Layer 3 depending on the needs of the original communication
VXLAN (Virtual Extensible LAN) is indeed a powerful technique for creating virtualized overlay networks. It's great for extending Layer 2 networks over a Layer 3 infrastructure
VXLAN use UDP for transport
Policy Plane - CiscotrustSec
Used for security and segmentation
Cisco TrustSec decouples access that is based strictly on IP addresses and VLANs by using logical groupings in a method known as Group-Based Access Control (GBAC).
The goal of Cisco TrustSec technology is to assign an SGT value to the packet at its ingress point into the network. An access policy elsewhere in the network is then enforced based on this tag information.
The fabric VXLAN encapsulation method is actually used by both the data plane and policy plane
Management Plane -Cisco DNA center
Orchestration, assurance, visibility, and management.
Cisco DNA Center is a foundational component of SD-Access, enabling automation of device deployments and configurations into the network to provide the speed and consistency required for operational efficiency.
Through its automation capabilities, the control plane, data plane, and policy plane for the fabric devices is easily, seamlessly, and consistently deployed.
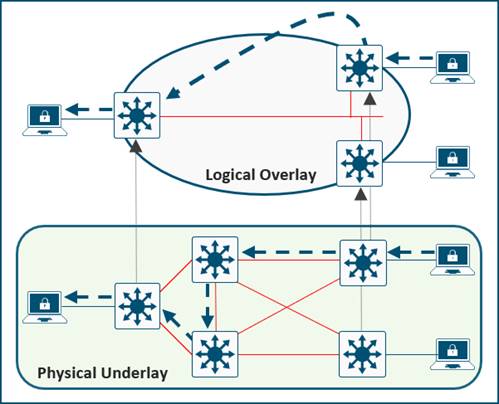
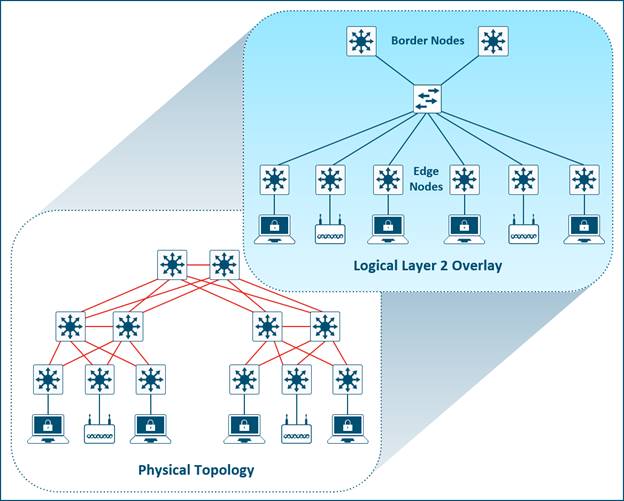
A fabric is simply an overlay network. Overlays are created through encapsulation, a process which adds additional header(s) to the original packet or frame. An overlay network creates a logical topology used to virtually connect devices that are built over an arbitrary physical underlay topology.
Overlay Network
An overlay network is created on top of the underlay network through virtualization (virtual networks). The data plane traffic and control plane signaling are contained within each virtualized network, maintaining isolation among the networks and an independence from the underlay network.
Multiple overlay networks can run across the same underlay network through virtualization. In SD-Access, the user-defined overlay networks are provisioned as a virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) instances that provide separation of routing tables.
LISP and VXLAN
 Reviewed by ohhhvictor
on
1:11:00 PM
Rating:
Reviewed by ohhhvictor
on
1:11:00 PM
Rating:
 Reviewed by ohhhvictor
on
1:11:00 PM
Rating:
Reviewed by ohhhvictor
on
1:11:00 PM
Rating:


















No comments: