Wireless security
Wireless security is the protection of devices and networks connected in a wireless environment. Without Wi-Fi security, a networking device such as a wireless access point or a router can be accessed by anyone using a computer or mobile device within range of the router's wireless signal.
- Supplicant is the host device that need to be authenticated.
- Authenticator is the relay device that connects Supplicant to the Authentication Server and controls the network access.
- Authentication Server is the AAA Server (Radius Server etc.).
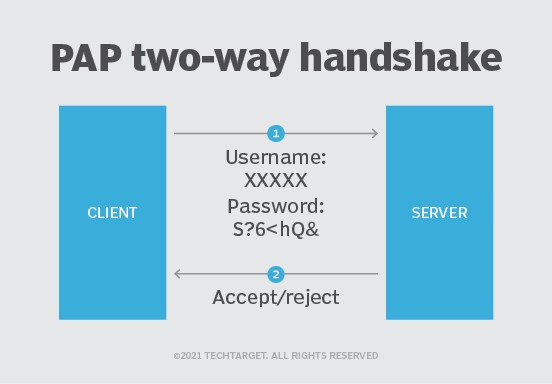
What is PAP?
Of the two Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) authentication methods, PAP is older. It was standardized in 1992 by way of IETF Request for Comments 1334. PAP is a client-server, password-based authentication protocol. Authentication occurs only one time at the beginning of a session establishment process.
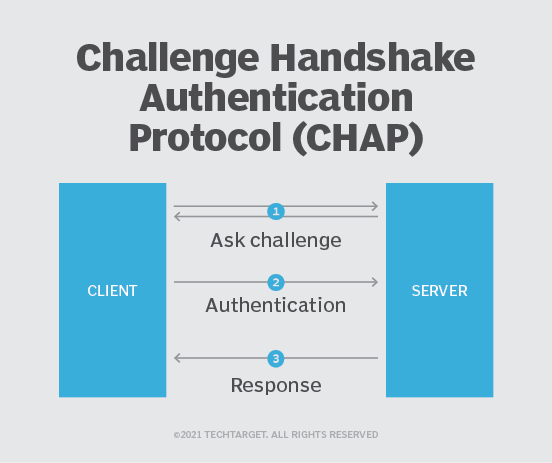
What is CHAP?
Instead of a two-way handshake, CHAP uses a three-way handshake and doesn't send the password across the network. CHAP uses an encrypted hash for which both the client and server know the shared secret key. This extra step helps eliminate the security weaknesses found in PAP.
Another difference is CHAP can be set up to do repeated midsession authentications. This is useful for certain PPP sessions that leave a port open even though the remote device has disconnected. In that case, someone else could pick up the connection midsession by establishing physical connectivity.
 Reviewed by ohhhvictor
on
12:00:00 PM
Rating:
Reviewed by ohhhvictor
on
12:00:00 PM
Rating:












No comments: